Biography
Dr. Donato Tedesco received his B.S. in Molecular and Cell Biology from La Sapienza University of Rome, Italy; followed by his doctoral degree in Biotechnology from the same institution in 1998. During that time, he studied the genetic mechanisms underlying tumorigenesis, with a focus on the identification of key regulators of the cell replication cycle G1/S and G1/G0 transitions. During his post-doctoral position in the Reed lab at the Scripps Research Institute, he studied the role of protein ubiquitylation in cancerogenesis. Between 2005-2007, he worked for Berlex/Schering AG on several projects aimed at the identification of targets for small molecule anti-cancer drugs in the ubiquitin/proteasome protein degradation pathway. In late 2007, Dr. Tedesco joined Cellecta where he has been responsible for the development and validation of the DECIPHER RNAi screening platform (www.decipherproject.net), and of the company’s CRISPR product and services portfolio.
Emerging Therapeutics Showcase:
Cellecta Inc.
A functional genomics solutions provider, focuses primarily on developing and implementing flexible and scalable broad-based screening and analysis approaches for drug target and biomarker discovery.
Clonal Analysis And Genetic Screening At A Single-Cell Level
Novel methods for profiling clonal composition and phenotypes of primary and metastatic lesions at the single-cell level are required to better understand tumorigenesis and develop anti-cancer drugs with unique mechanisms of action. To this end, we show how combining a genetic screen with cell barcoding can significantly improve gene function analysis in cancer cell models.
Session Abstract – PMWC 2020 Silicon Valley
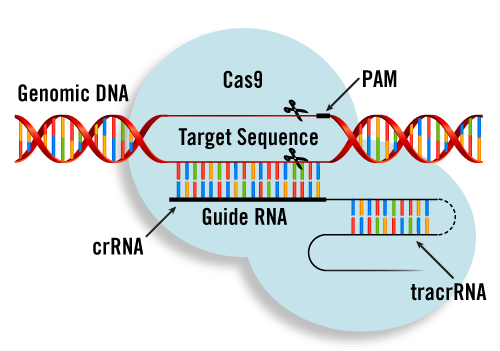
The PMWC 2020 Emerging Therapeutics Showcase will provide a 15-minute time slot for selected companies and researchers in the CRISPR, Cell and Gene Therapy fields. Major advancements in safer cell- and gene-level editing technologies are bringing us closer toward cures for life-threatening disorders, from cancer to HIV to Huntington’s disease. Cell therapy, in which cellular material such as T cells capable of fighting cancer cells, is injected into a patient, has been demonstrated safe and effective. The popular new CRISPR tool that has been used to edit the genetic code of nearly any organism will have an enormous impact on human health. More than a dozen clinical trials employing CRISPR on human cells are already underway.